WARNING
Are you 21 or older ?
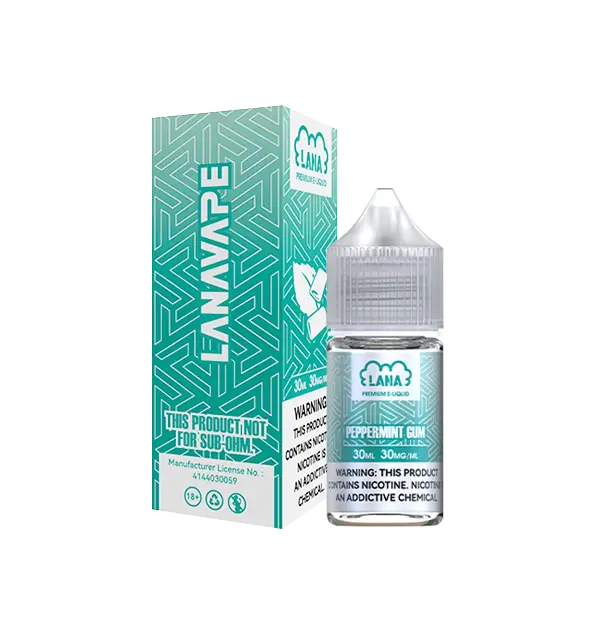
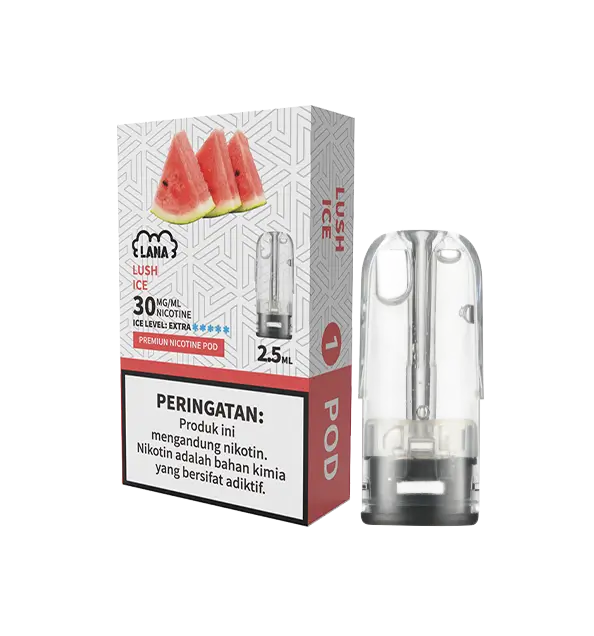
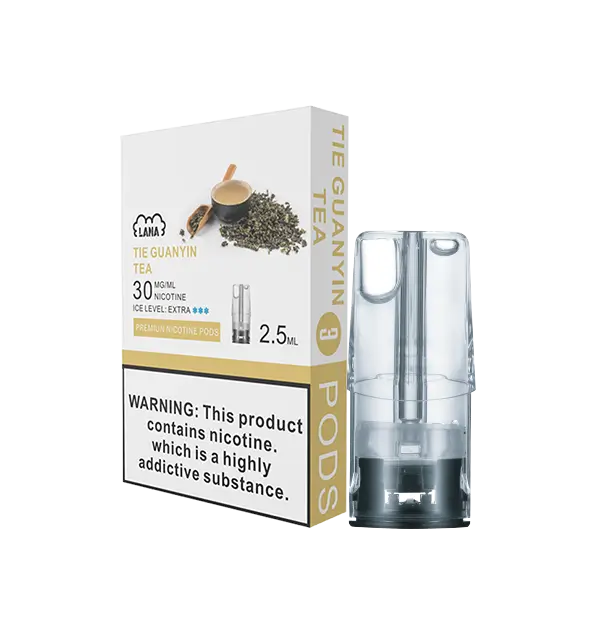
This product contains nicotine.Nicotine is an addictive chemical. Only for adults, MINORS are prohibited from buying e-cigarette.
Under 21
21+
404
Oops!
Request Fail!
The page you are looking for does not exist!
Tel: +8619926442584
Email: inquiry@lanavape.com
Service Time: 9:00am-12:30am, 2:00pm-6:30pm, Monday-Friday GMT+8
Address: 11F, Block B, Xingzhan Plaza, No. 446 Nanhuan Road, Shajing Town, Bao'an District, Shenzhen, China.
Payoneer: 84652183@qq.com
Paypal: dines@vip.qq.com、84652183@qq.com
Business Contact: inquiry@lanavape.com
Customer Service: inquiry@lanavape.com
Marketing Cooperation: inquiry@lanavape.com
Service Time: 9:00am-12:30am, 2:00pm-6:30pm, Monday-Friday GMT+8
Address: 11F, Block B, Xingzhan Plaza, No. 446 Nanhuan Road, Shajing Town, Bao'an District, Shenzhen, China.
Payoneer: 84652183@qq.com
Paypal: dines@vip.qq.com、84652183@qq.com